The cat Linux command is used to display file contents, for example if I quickly wanted to see the contents of a text file I would use the cat command to dump the output to the console or pipe it to another command.
Situations when the cat Linux command would used
- How To dump the contents of a file and pipe into another Linux command
- Show / display text files in Linux
- Display a text file with line numbers on Linux
- Redirect the output of a file into another file on the Linux command line
Linux cat Command Example 1
cat blah.txt
This would then display the entire contents of the file to the console, so for larger files you might want to pipe it through less or more:
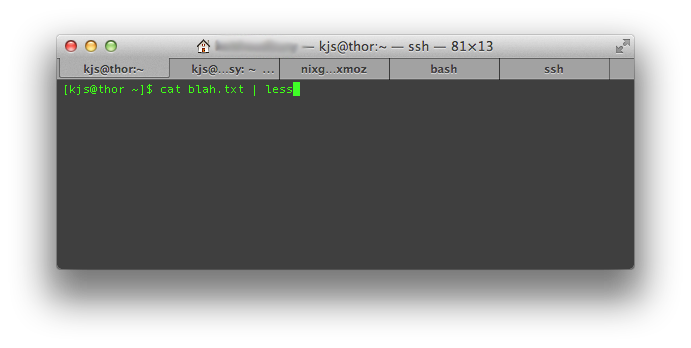
Cat Command piped through less or more
cat blah.txt | less
If you only want to view the top of the file you might want to use the head command and likewise if you want view the bottom of a large file I would recommend using the tail command.
Cat Command Options
The cat command has the following options to allow more advanced functionality.
-A, --show-all
equivalent to -vET
-b, --number-nonblank
number nonempty output lines
-e equivalent to -vE
-E, --show-ends
display $ at end of each line
-n, --number
number all output lines (handy for script parsing)
-s, --squeeze-blank
suppress repeated empty output lines
-t equivalent to -vT
-T, --show-tabs
display TAB characters as ^I
-u (ignored)
-v, --show-nonprinting
use ^ and M- notation, except for LFD and TAB
--help display this help message and exit
--version
show cat version information and exit
Cat Command Install
How to install the cat command on RPM / DPKG based Linux systems.
Install Cat via YUM (CentOS, RHEL, Fedora)
If the cat command is missing on your RHEL based system (CentOS, RHEL, Fedora etc) then you can install it with the following YUM command:
yum install coreutils
Install Cat via APT (Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint)
To install cat on DPKG based distros, Ubuntu, Debian, Linux Mint etc enter the following command (on Mint Ubuntu you will need to prefix with sudo).
apt-get install coreutils