pfSense 2.0 incorporates a number of useful services, a number of which will be the focus of future articles on this site. In this article, I will cover the Optimized Link State Routing Protocol (OLSR): what it is, why it is useful, and how to enable pfSense OLSR.
OLSR Explained
The Optimized Link State Routing Protocol (OLSR) is an IP routing protocol optimized for mobile ad hoc networks, which can also be used on other wireless ad hoc networks. It was defined in RFC 3626 in October 2003. Mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) are self-configuring, infrastructureless network of mobile devices connected by wireless. OLSR is a proactive link-state routing protocol which uses hello and topology control (TC) messages to discover and then disseminate link state information throughout the mobile ad hoc network. Individual nodes use this topology to computer next hop destinations for all nodes in the network using shortest hop forwarding paths. Unlike link-state routing protocols such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), in which there is a designated router on every link to perform flooding of topology information, the OLSR protocol uses Hello messages to discover 2-hop neighbor information and perform a distributed election of a set of multipoint relays (MPRs).
MPRs are the key concept used in the OLSR protocol. The MPRs forward broadcast messages during the flooding process. This technique substantially reduces the message overhead as compared to a classical flooding mechanism, where every node retransmits each message when it receives the first copy of the message. In OLSR, link state information is generated only by nodes elected as MPRs. As a result, a second optimization is achieved by minimizing the number of control messages flooded in the network. As a third optimization, an MPR node may choose to report only links between itself and its MPR selectors. Thus, unlike in the classic link state algorithm, partial link state information is distributed in the network and used for route calculation.
Enabling pfSense OLSR
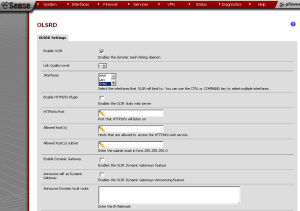
In order to enable pfSense OLSR via the pfSense web GUI, first navigate to Services -> OLSR and check the “Enable OLSR” check box. At “Link Quality Level“, you can keep this at its default setting unless you want to allow a lower level of link quality. At “Interface“, choose an interface (use the CTRL key to select multiple interfaces). Then press the “Save” button to save the changes.
Additional pfSense OLSR Options
Now, pfSense OLSR will be enabled. However, there are several other options for OLSR in pfSense, the most notable of which is the HTTPInfo plugin. Enabling the HTTPInfo plugin allows us to view and monitor the status of the OLSR mesh network. You can enable this plugin by checking the “Enable HTTPInfo Plugin” check box. Below that, we need to specify an “HTTPInfo Port” (the port that HTTPInfo will listen on), and specify “Allowed Host(s)” (hosts that are allowed to access the HTTPInfo service). We also need to specify the subnet mask at “Allowed Host(s) Subnet“.
There are a few other pfSense OLSR options that should be noted. Checking “Enable Dynamic Gateway” enables the OLSR Dynamic Gateways plugin. This plugin dynamically detects when nodes obtain and lose Internet connectivity and updates the host and network association (HNA) information based on this. The main object of this plugin is to poll for an Internet route and add or remove such a route from the local HNA set if a change is detected. The “Announce self as Dynamic Gateway” enables the OLSR Dynamic Gateways Announcing feature. At “Announce Dynamic local route“, enter the IP address and netmask of the dynamic local route. “Ping” allows you to specify a host to ping to ensure connectivity, and “Poll” specifies how long to look for an internet gateway in seconds. Finally, “Enable Secure mode” allows you to enable the secure mode, and “Key” holds the secure OLSR key information.